Abstract:
Diabetes is a global health issue affecting millions of lives worldwide. As the number of people with diabetes continues to rise, effective management of the condition has become increasingly important. Blood glucose monitoring stands as a cornerstone in the management of diabetes, playing a critical role in assessing treatment efficacy, adjusting therapeutic plans, and preventing complications.
- Introduction**
The prevalence of diabetes and the significance of blood glucose monitoring in its management are highlighted. - Definition and Purpose of Blood Glucose Monitoring**
- Definition: Blood glucose monitoring refers to the regular testing of blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes using certain technical methods.
- Purpose: To promptly understand blood sugar fluctuations, providing a basis for treatment and assisting patients and doctors in evaluating the effectiveness of treatments, adjusting therapeutic plans, and preventing the onset of complications.
- Methods of Blood Glucose Monitoring**
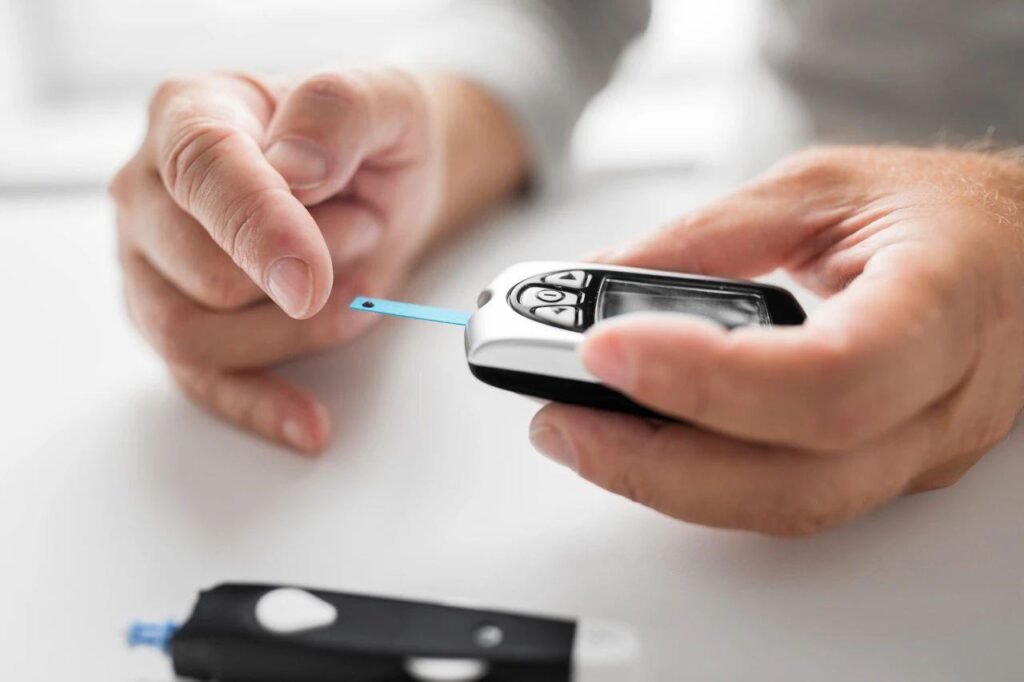
- Capillary Blood Glucose Monitoring (SMBG): Rapid blood glucose testing conducted via a glucometer, which can be performed at home or anywhere.
- Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Testing: An indicator reflecting the average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Continuous monitoring of glucose levels in the interstitial fluid through a sensor.
- The Role of Blood Glucose Monitoring in Diabetes Management**
- Assessing Treatment Effectiveness: By monitoring changes in blood glucose levels, doctors can evaluate the effectiveness of current treatment plans.
- Adjusting Treatment Plans: Based on the results of blood glucose monitoring, doctors can adjust medication dosages or recommend lifestyle changes.
- Preventing Complications: Long-term good blood sugar control can reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Clinical Significance of Blood Glucose Monitoring**
- Short-term Blood Sugar Control
- Long-term Blood Sugar Control
- Risk Assessment for Hypoglycemia
- Challenges and Strategies in Blood Glucose Monitoring**
- Patient Compliance Issues
- Selection and Application of Monitoring Technology
- Data Interpretation and Clinical Decision-Making
- Future Prospects**
- Development of Non-invasive Blood Glucose Monitoring Technology
- Application of Smart Monitoring Devices
- Development of Individualized Blood Glucose Control Strategies
- Conclusion**
Emphasizing the central role of blood glucose monitoring in diabetes management, and the potential of future developments.
Body (Partial):**
Diabetes is a global health issue affecting millions of lives worldwide. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the number of people with diabetes is growing rapidly, with projections estimating nearly 700 million individuals affected by 2045. This trend underscores the importance of effective diabetes management, where blood glucose monitoring is fundamental.
Blood Glucose Monitoring: Definition and Purpose
Blood glucose monitoring involves the regular testing of blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes using certain technical methods. Its primary purpose is to promptly understand blood sugar fluctuations, providing a basis for treatment and assisting patients and doctors in evaluating the effectiveness of treatments, adjusting therapeutic plans, and preventing complications.
Methods of Blood Glucose Monitoring
Blood glucose monitoring can be conducted through various methods, including but not limited to:
- Capillary Blood Glucose Monitoring (SMBG): Rapid blood glucose testing via a glucometer, which can be performed at home or anywhere.
- Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Testing: An indicator that reflects the average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Continuous monitoring of glucose levels in the interstitial fluid through a sensor.
The Role of Blood Glucose Monitoring in Diabetes Management
Blood glucose monitoring is crucial for individuals with diabetes as it not only helps them understand their blood sugar control status but also:
- Assesses Treatment Effectiveness: By monitoring changes in blood glucose levels, doctors can evaluate the effectiveness of current treatment plans.
- Adjusts Treatment Plans: Based on the results of blood glucose monitoring, doctors can adjust medication dosages or recommend lifestyle changes.
- Prevents Complications: Long-term good blood sugar control can reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Conclusion
Blood glucose monitoring is an indispensable part of diabetes management. With technological advancements, future blood glucose monitoring is expected to become more convenient and accurate, aiding in the realization of individualized treatment and management strategies, thereby improving the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.