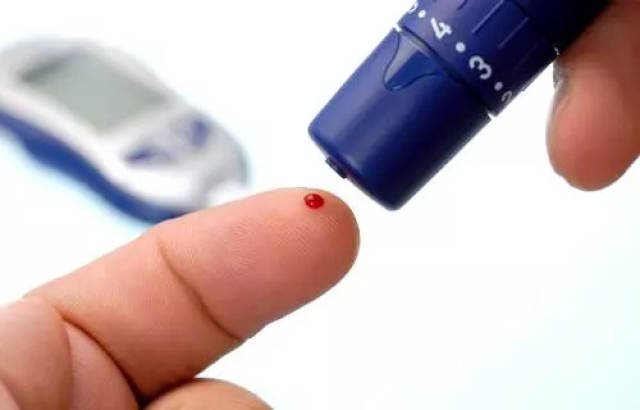
1. Introduction
With the global increase in the number of diabetes patients, blood glucose monitoring has become a central aspect of diabetes management. Accurately using a glucometer not only helps patients keep track of their blood glucose levels in real-time but also effectively prevents complications. However, many people overlook key details during daily use, leading to inaccurate measurements and potentially impacting their health management. As an SEO expert, I will provide a detailed guide on the correct use of a glucometer and offer suggestions on optimizing this article for better search engine rankings.
2. The Basics and Importance of Glucometers
2.1 How Glucometers Work
A glucometer is a portable device that analyzes the glucose concentration in a blood sample to display blood glucose levels. Most glucometers use electrochemical sensor technology, allowing for accurate blood glucose readings in a short time.
2.2 The Importance of Blood Glucose Monitoring
Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial for diabetes patients. It helps them understand fluctuations in their blood glucose levels, guiding their diet, exercise, and medication. Timely and accurate monitoring can prevent acute complications caused by hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia and provide valuable data for doctors to adjust treatment plans.
3. Correct Steps for Using a Glucometer
3.1 Preparation
- Choosing the Right Time: Common monitoring times include fasting, post-meal, and before bed. Patients should determine daily testing times based on their doctor’s recommendations.
- Hand Hygiene: Ensure hands are clean before testing. Wash thoroughly with warm water and soap to avoid any substances that could affect the results.
3.2 Blood Sampling
- Choosing a Sampling Site: Most people choose the side of the fingertip, where blood circulation is better, allowing for a quick and sufficient blood sample.
- Using a Lancet: Quickly prick the skin with a sterilized lancet to minimize pain. Lancets should be used only once to avoid infection.
3.3 Blood Sample Analysis
- Applying the Test Strip: Insert the test strip into the glucometer, ensuring correct operation. Gently touch the blood sample to the strip’s absorbing end, allowing it to absorb enough blood.
- Reading the Results: The glucometer will display the blood glucose level within a short time. Ensure the reading is stable before recording the results.
3.4 Recording and Analyzing Data
- Regular Recording: Log daily blood glucose readings, including the time and any relevant conditions (e.g., eating, exercise). This helps patients and doctors track trends and adjust treatment plans.
- Consulting with a Doctor: Regularly discuss your glucose records with your doctor, especially if there are unusual fluctuations that need to be addressed.
4. Common Misconceptions and Solutions
4.1 Misconception 1: Ignoring Hand Hygiene
Many users do not thoroughly clean their hands before testing, leading to contaminated results. It is recommended to wash hands thoroughly before each test to avoid any contaminants.
4.2 Misconception 2: Reusing Lancets or Test Strips
Some patients reuse lancets or test strips to save costs. This not only reduces accuracy but also increases the risk of infection. Always use a new lancet and test strip for each test.
4.3 Misconception 3: Neglecting Device Calibration
Glucometers need regular calibration to ensure accuracy. Check the device manual regularly, follow calibration instructions, and replace the device when necessary.
5. Factors Affecting Glucometer Accuracy
5.1 Environmental Temperature
Extreme temperatures can affect the accuracy of a glucometer. Check the manual for the appropriate operating temperature range and try to measure blood glucose at room temperature.
5.2 Quality of Blood Sample
Insufficient blood sample volume or air bubbles in the sample can lead to inaccurate readings. Ensure you collect enough blood and avoid introducing air into the test strip.
5.3 Storage of Test Strips
Store test strips in a dry, dark environment, avoiding heat and moisture. Replace expired or damaged strips promptly.
6. SEO Optimization Suggestions
6.1 Strategic Keyword Placement
Distribute relevant keywords such as “glucometer usage,” “accurate use of glucometer,” and “blood glucose monitoring” throughout the article. This will not only enhance the article’s ranking in search engines but also help target users find the information more easily.
6.2 Use of Internal and External Links
Include links to authoritative medical websites as well as internal links to other related content within your site. This will help increase page authority and improve user experience.
6.3 Effective Use of Multimedia
Consider adding related images, videos, or infographics to the article to visually demonstrate the steps for using a glucometer or highlight common misconceptions. This will enhance page engagement and user time on site, further boosting SEO performance.
6.4 Regular Content Updates
Medical content needs to be regularly updated to maintain accuracy and relevance. Ensure the information in the article aligns with the latest medical research and guidelines, and continually optimize the content based on user feedback.
7. Conclusion
Accurate use of a glucometer is vital for the daily management of diabetes. Patients should follow the correct usage steps, avoid common misconceptions, and regularly consult with their doctor to optimize their treatment plan.